Multiplexing Techniques
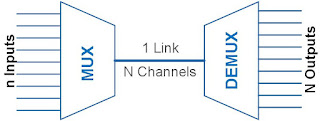
What is a Multiplexing?
- Sharing the link among multiple users
Introduction to Multiplexing
What is Multiplexing Techniques?
Multiplexing is the process of combining multiple signals into one signal, over a shared medium. If analog signals are multiplexed, it is Analog Multiplexing and if digital signals are multiplexed, that process is Digital Multiplexing.
Types of Multiplexing Techniques
Analog Multiplexing:
- Frequency Division Multiplexing
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing
- Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
In analog multiplexing, the most used technique is Frequency Division Multiplexing FDM. This technique uses various frequencies to combine streams of data, for sending them on a communication medium, as a single signal.
Concept and Process:
In FDM, the total bandwidth is divided to a set of frequency bands that do not overlap. The frequency bands are separated from one another by strips of unused frequencies called the guard bands, to prevent overlapping of signals.
The combined signal is transmitted over the communication channel, At the receiving end, the individual signals are extracted from the combined signal by the process of demultiplexing (DEMUX).
Example: A traditional television transmitter, which sends a number of channels through a single cable, uses FDM.
2. Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
Wavelength Division Multiplexing is an analog technique, in which many data streams of different wavelengths are transmitted in the light spectrum.
Concept and Process:
In WDM, the optical signals from different sources or (transponders) are combined by a multiplexer, which is essentially an optical combiner. They are combined so that their wavelengths are different.
The combined signal is transmitted via a single optical fiber strand. At the receiving end, a demultiplexer splits the incoming beam into its components and each of the beams is send to the corresponding receivers.
Example: Optical fibre Communications use the WDM technique, to merge different wavelengths into a single light for the communication.
Digital Multiplexing
- Time Division Multiplexing:
Example: It is widely used in telephone and cellular networks.
TDM and FDM both are multiplexing techniques. In TDM, syncronization pulse is important whereas in FDM, Guard Band is required
Applications of Multiplexing
The applications of multiplexing include the following.
- Analog Broadcasting
- Digital Broadcasting
- Telephony
- Video Processing
- Telegraphy




Very informative
ReplyDeletethank you!
DeleteSuch a amazing page and very informative
ReplyDeletethank you!
DeleteBrilliantly explained, like to see such more blogs from you👍💯
ReplyDeletethanks!
DeleteVery well explained 👍👌
ReplyDeletethanks!
Delete👍👍👍👍
ReplyDeleteWell explained
ReplyDeletethanks!
DeleteVery helpfull for me Tysm for such good information👐💯
ReplyDeletethank you!
DeleteGreat source of knowledge for newbies to d field
ReplyDeletethanks!
DeleteNice work
ReplyDeleteSuch a innovative information!!
ReplyDeletethanks!
DeleteNice work! 💯💯
ReplyDeleteVery well written 💯
ReplyDeleteVery well explained!
ReplyDeletethank you!
DeleteNice 👍
ReplyDeleteWell written 👍🏻
ReplyDeletethank you!
DeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete👍🙌
ReplyDeletethank you!
DeleteWell explained..👍
ReplyDeletethank you!
DeleteBest👍
ReplyDeleteGreat explanation !!
ReplyDeleteVery good
ReplyDeleteGreat 🙌🙌
ReplyDeleteVery well written 👍👍
ReplyDeletethanks!
DeleteInformative.....nice
ReplyDeletethanks!
DeleteNice
ReplyDeletethanku1
DeleteBest 👍
ReplyDeleteAmazing!
ReplyDeletethank u!
DeleteAwesome and informative blog!!
ReplyDeletethank u!
DeleteVery nice and informative 👍
ReplyDeletethank u!
Deletethanku!
ReplyDeleteBrilliantly explained 💯👏
ReplyDeleteGreat work!
ReplyDelete